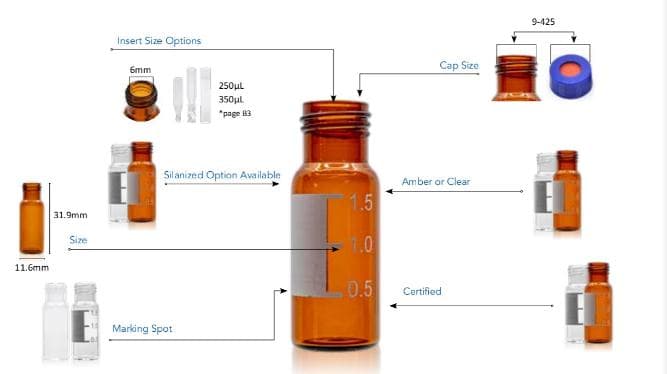
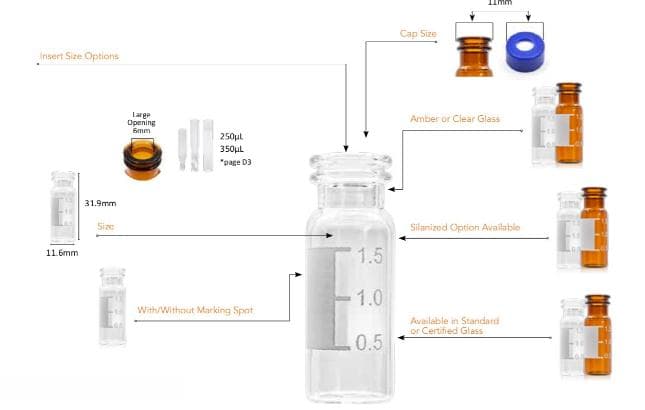
-
Jan 1, 2018 · The most commonly employed techniques for sterilization are thermal sterilization, filtration, chemical sterilization, and irradiation. In the case of thermal sterilization, it is the only method by which the sterilization of liquid fermentation media is possible.
-
1. Prepare the items for sterilization (Fig #1): glass bottles with caps - washed, air-dried completely, capped with cap half-loosened, autoclave tape on top of lid. plastic large centrifuge bottles with caps - washed, air-dried completely, capped with cap very loosely covering the opening and NOT tightened, autoclave tape on top of lid.
-
Nov 8, 2021 · In the biopharmaceutical industry, to the authors’ knowledge, tray drying is mostly used for the manufacture of drug substance, drug product intermediates, or APIs. Tray drying is generally conducted either in disposable plastic or reusable metal trays. Freeze-drying in trays has some specific considerations compared to vial freeze-drying.
-
Dec 7, 2020 · The first factor is the stopper; formulation, design, siliconization, and sterilization have an effect. Generally, the softer the stopper and the thinner the diaphragm, the lower the level of cores/fragments. Also, siliconization may lower the level of cores/fragments. Regarding sterilization, steam processed stoppers have lower levels as
-
Jan 1, 2020 · Virus safety in the biopharmaceutical industry has evolved over the years. Virus filtration has and continues to play a key role in the mission of process safety for biopharmaceutical drug products. These filters are added into the process to robustly remove both endogenous and adventitious viruses via size exclusion (viruses are retained and
-
Jul 15, 2015 · Abstract. Steam sterilization is a critical process in the pharmaceutical and related industries. Modern autoclaves are computer-controlled and reliably provide a defined sterilization cycle. This
-
An ideal biological monitor of the sterilization process should be easy to use, be inexpensive, not be subject to exogenous contamination, provide positive results as soon as possible after the cycle so that corrective action may be accomplished, and provide positive results only when the sterilization parameters (e.g., steam-time, temperature
-
Depending on the formulation, the stoppers may be able to be sterilized by irradiation. Aseptic fill/finish processes can very from a clinical hand fill, to semi-automated mono-block, to a high speed filling lines. Filling equipment systems can be characterized as either “Open,” “Barrier,” “Isolator” and “RABS.”.
-
vial system Does not mention BUDs other than following the manufacturer’s instructions for handling and storing Docking of the proprietary bag and vial system for future activation • This is considered compounding and must be performed in accordance with this chapter (ISO Class 5 environment) • BUDs must not be longer than the
-
Sterilization Integrity Testing Fit for Use 8 Elements of a Sterile Filtration Validation Sterile Filter Master Plan Prove the filter meets all requirements within product & process conditions. Prove the filter does not adversely affect the process stream. Prove the sterilization method is effective and does not compromise the filter.
-
Feb 29, 2016 · The example in Figure 1 (page 00) shows vial filling in an open design RABS line. Risk zones in risk assessments. It is good practice to segregate the filling line into zones that have a primary process function and related interventions so that the FMEA risk analysis can be targeted zone by zone in a manageable way.
-
The first term is sterile. Something is considered sterile when it is “free from viable (live) microorganisms”. The second term is sterilization. Sterilization is “a validated process by which an article, surface, or medium is freed of all living microorganisms, either in the vegetative or spore state”. The third term is sterility.
-
Apr 1, 2010 · Headspace GCâ MS chromatographic conditions. Separate glass vials were filled with one of the 11 formulations listed in Table 1 and crimp-sealed with rubber stoppers. The stoppered vials containing various formulations were inverted and then stored at 40 °C and 75% RH. After one month, the formulations were tested for volatile, semi-volatile
-
Jan 1, 2013 · Aseptic processing refers to the various techniques that go into ensuring that the product is free of contaminants, thereby reducing the risk of infection to the patient. Aseptic processing, is the processing of drug components, drug product containers, and excipients in a manner that precludes microbial contamination of the final sealed product.
-
Oct 1, 2018 · Regulatory feedback has resulted in a major shift in how the biopharmaceutical industry looks at raw materials and their management. Most major manufacturers are applying the principles of risk analysis and good science towards identification of critical raw materials and their analytical characterization.